kafka是一个分布式的消息中间件,目前应用十分广泛。看源码不仅可以了解其底层的细节,同时,在看代码时,也能跟着大神们学到很多的编程技巧。
KafkaProducer的使用 在Kafka中,Client端是由Java实现的,Server端是Scala实现的。下面我们从Client端开始,分析一下Kafaka中的Producer模型。开始之前我们先看一下怎么向Topic中生产数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer;import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord;import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.Producer;import java.util.Properties;public class ProducerTest {private static String topicName;private static int msgNum;private static int key;public static void main (String [] args) new Properties ();put ("bootstrap.servers" , "127.0.0.1:9092,127.0.0.2:9092" );put ("key.serializer" ,"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer" );put ("value.serializer" ,"org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer" );"test" ;10 ; String , String > producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props);for (int i = 0 ; i < msgNum; i++) {String msg = i + " This is matt's blog." ;send (new ProducerRecord <String , String >(topicName, msg));close ();
从上面可以看到如何向Topic中生产数据,Kafka在这方面封装的很好,只需要两步就可以完成操作:
1. 初始化KafkaProducer类
2. 调用send接口发送数据
下面围绕着send接口开始展开。
KafkaProducer中的send方法 用户使用producer.send发送数据,我们看一下send()的实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Override public Future<RecordMetadata> send(ProducerRecord<K, V> record) {return send(record, null );@Override public Future<RecordMetadata> send(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {this .interceptors == null ? record : this .interceptors.onSend(record);return doSend(interceptedRecord, callback);
接口最后会走一个doSend()方法,接着追进去
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 private Future<RecordMetadata> do Send(ProducerRecord<K, V> record , Callback callback ) {try {OnMetadata(record .topic () , record.partition() , maxBlockTimeMs);Math .0 , maxBlockTimeMs - clusterAndWaitTime.waitedOnMetadataMs);[] serializedKey;try {() , record.key() );new SerializationException("Can't convert key of class " + record .key () .getClass() .getName() +" to class " + producerConfig.getClass(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG) .getName() +" specified in key.serializer" );[] serializedValue;try {() , record.value() );new SerializationException("Can't convert value of class " + record .value () .getClass() .getName() +" to class " + producerConfig.getClass(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG) .getName() +" specified in value.serializer" );int partition = partition(record, serializedKey, serializedValue, cluster);int serializedSize = Records.LOG_OVERHEAD + Record .Size(serializedKey , serializedValue ) ;ValidRecordSize(serializedSize ) ; new TopicPartition(record .topic () , partition);() == null ? time.milliseconds() : record.timestamp() ; "Sending record {} with callback {} to topic {} partition {}" , record, callback, record.topic() , partition); == null ? callback : new InterceptorCallback<>(callback, this.interceptors, tp);if (result.batchIsFull || result.newBatchCreated) {"Waking up the sender since topic {} partition {} is either full or getting a new batch" ,record.topic() ,partition);() ;"Exception occurred during message send:" , e);if (callback != null)Completion(null , e ) ;() ;if (this.interceptors != null)SendError(record , tp , e ) ;new FutureFailure(e ) ;() ;if (this.i nterceptors != null)SendError(record , tp , e ) ;new InterruptException(e ) ;() ;"buffer-exhausted-records" ).record() ;if (this.interceptors != null)SendError(record , tp , e ) ;() ;if (this.interceptors != null)SendError(record , tp , e ) ;if (this.interceptors != null)SendError(record , tp , e ) ;
在 dosend() 方法的实现上,一条 Record 数据的发送,可以分为以下五步:
1. 确认数据要发送到的 topic 的 metadata 是可用的(如果该 partition 的 leader 存在则是可用的,如果开启权限时,client 有相应的权限),如果没有 topic 的 metadata 信息,就需要获取相应的 metadata;
2. 序列化 record 的 key 和 value;
3. 获取该 record 要发送到的 partition(可以指定,也可以根据算法计算);
4. 向 accumulator 中追加 record 数据,数据会先进行缓存;
5. 如果追加完数据后,对应的 RecordBatch 已经达到了 batch.size 的大小(或者batch 的剩余空间不足以添加下一条 Record),则唤醒 sender 线程发送数据。
数据的发送过程,可以简单总结为以上五点,下面会这几部分的具体实现进行详细分析。
发送的过程详解 Producer 通过 waitOnMetadata() 方法来获取对应 topic 的 metadata 信息,这部分后面会单独抽出一篇文章来介绍,这里就不再详述,总结起来就是:在数据发送前,需要先该 topic 是可用的。
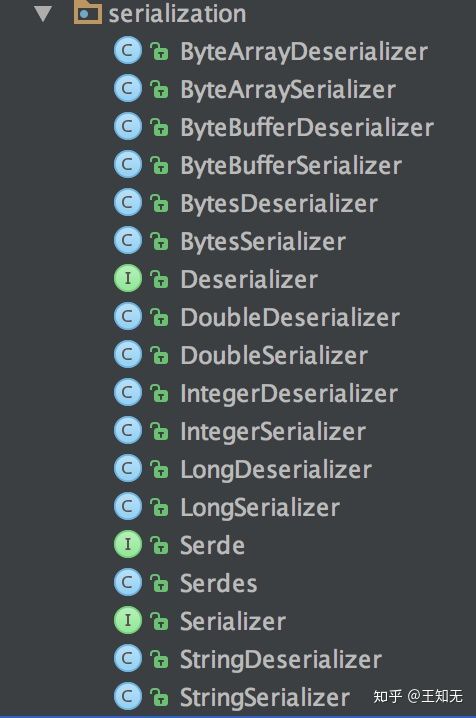
key 和 value 的序列化 Producer 端对 record 的 key 和 value 值进行序列化操作,在 Consumer 端再进行相应的反序列化,Kafka 内部提供的序列化和反序列化算法如下图所示:
Kafka serialize & deserialize
当然我们也是可以自定义序列化的具体实现,不过一般情况下,Kafka 内部提供的这些方法已经足够使用。
获取 partition 值 关于 partition 值的计算,分为三种情况:
指明 partition 的情况下,直接将指明的值直接作为 partiton 值;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 // 当 record 中有 partition 值时,直接返回,没有的情况下调用 partitioner 的类的 partition 方法去计算(KafkaProducer.class )int partition (ProducerRecord<K, V> record , byte[] serializedKey, byte[] serializedValue, Cluster cluster ) {Integer partition = record .partition ();return partition != null ?partition :partition (record .topic(), record .key(), serializedKey, record .value (), serializedValue, cluster );
Producer 默认使用的partitioner是org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.DefaultPartitioner,用户也可以自定义 partition 的策略,下面是这个类两个方法的具体实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {ForTopic(topic ) ;int numPartitions = partitions.size() ;if (keyBytes == null) {int nextValue = nextValue(topic ) ; PartitionsForTopic(topic ) ;if (availablePartitions.size() > 0 ) {int part = Utils .to Positive(nextValue ) % availablePartitions.size() ;() ;else {Utils .to Positive(nextValue ) % numPartitions;else {Utils .to Positive(Utils.murmur2 (keyBytes ) ) % numPartitions; private int nextValue(String topic ) {if (null == counter) { new AtomicInteger(new Random() .nextInt() );IfAbsent(topic , counter ) ;if (currentCounter != null) {AndIncrement() ;
这就是 Producer 中默认的 partitioner 实现。
向 accumulator 写数据 Producer 会先将 record 写入到 buffer 中,当达到一个 batch.size 的大小时,再唤起 sender 线程去发送 RecordBatch(第五步),这里先详细分析一下 Producer 是如何向 buffer 中写入数据的。
Producer 是通过 RecordAccumulator 实例追加数据,RecordAccumulator 模型如下图所示,一个重要的变量就是 ConcurrentMap<TopicPartition, Deque> batches,每个 TopicPartition 都会对应一个 Deque,当添加数据时,会向其 topic-partition 对应的这个 queue 最新创建的一个 RecordBatch 中添加 record,而发送数据时,则会先从 queue 中最老的那个 RecordBatch 开始发送。
1 
Producer RecordAccumulator 模型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 [] key,[] value,AndGet() ;try {OrCreateDeque(tp ) ;if (closed)new IllegalStateException("Cannot send after the producer is closed." ) ;try Append(timestamp , key , value , callback , dq ) ; if (appendResult != null)int size = Math .Record .Size(key , value ) );"Allocating a new {} byte message buffer for topic {} partition {}" , size, tp.topic() , tp.partition() );if (closed)new IllegalStateException("Cannot send after the producer is closed." ) ;try Append(timestamp , key , value , callback , dq ) ;if (appendResult != null) {MemoryRecords .new RecordBatch(tp , recordsBuilder , time .milliseconds () );Utils .Null(batch .tryAppend (timestamp , key , value , callback , time .milliseconds () ));Last(batch ) ;new RecordAppendResult(future , dq .size () > 1 || batch.isFull() , true );AndGet() ;
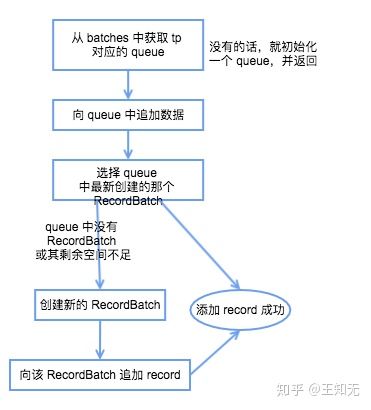
总结一下其 record 写入的具体流程如下图所示:
Producer RecordAccumulator record 写入流程
获取该 topic-partition 对应的 queue,没有的话会创建一个空的 queue;
发送 RecordBatch 当 record 写入成功后,如果发现 RecordBatch 已满足发送的条件(通常是 queue 中有多个 batch,那么最先添加的那些 batch 肯定是可以发送了),那么就会唤醒 sender 线程,发送 RecordBatch。
sender 线程对 RecordBatch 的处理是在 run() 方法中进行的,该方法具体实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 void run(long now) {this .accumulator.ready(cluster, now);if (!result.unknownLeaderTopics.isEmpty()) {for (String topic : result.unknownLeaderTopics)this .metadata.add(topic);this .metadata.requestUpdate();Long .MAX_VALUE;while (iter.hasNext()) {if (!this .client.ready(node, now)) {this .client.connectionDelay(node, now));this .accumulator.drain(cluster, result.readyNodes, this .maxRequestSize, now);if (guaranteeMessageOrder) {for (List<RecordBatch> batchList : batches.values()) {for (RecordBatch batch : batchList)this .accumulator.mutePartition(batch.topicPartition);this .accumulator.abortExpiredBatches(this .requestTimeout, now);for (RecordBatch expiredBatch : expiredBatches)this .sensors.recordErrors(expiredBatch.topicPartition.topic(), expiredBatch.recordCount);if (!result.readyNodes.isEmpty()) {"Nodes with data ready to send: {}" , result.readyNodes);0 ;this .client.poll(pollTimeout, now);
这段代码前面有很多是其他的逻辑处理,如:移除暂时不可用的 node、处理由于元数据不可用导致的超时RecordBatch,真正进行发送发送RecordBatch的是sendProduceRequests(batches, now)这个方法,具体是:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 private void sendProduceRequests(Map<Integer, List<RecordBatch>> collated , long now ) {for (Map.Entry<Integer, List<RecordBatch>> entry : collated.entrySet() )ProduceRequest(now , entry .getKey () , acks, requestTimeout, entry.getValue() );private void sendProduceRequest(long now , int destination , short acks , int timeout , List<RecordBatch> batches ) {new HashMap<>(batches.size() );new HashMap<>(batches.size() );for (RecordBatch batch : batches) {() );new ProduceRequest.Builder(acks , timeout , produceRecordsByPartition ) ;new RequestCompletionHandler() {Complete(ClientResponse response ) {ProduceResponse(response , recordsByPartition , time .milliseconds () );Integer .to String(destination ) ;new ClientRequest(nodeId , requestBuilder , now , acks != 0, callback ) ;"Sent produce request to {}: {}" , nodeId, requestBuilder);
这段代码就简单很多,总来起来就是,将 batches 中 leader 为同一个 node 的所有 RecordBatch 放在一个请求中进行发送。
最后 本文是对 Kafka Producer 端发送模型的一个简单分析,下一篇文章将会详细介绍 metadata 相关的内容,包括 metadata 的内容以及在 Producer 端 metadata 的更新机制。
转自:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/66190242